Summary
This is the final post in a three-part series configuring Elasticsearch (ES) cross-cluster replication and search. The first two posts set up two distinct ES clusters: one implemented in Kubernetes (ECK), and the other in Docker.
- Part 1: West Cluster Build
- Part 2: East Cluster Build
- Part 3: Replication + Search
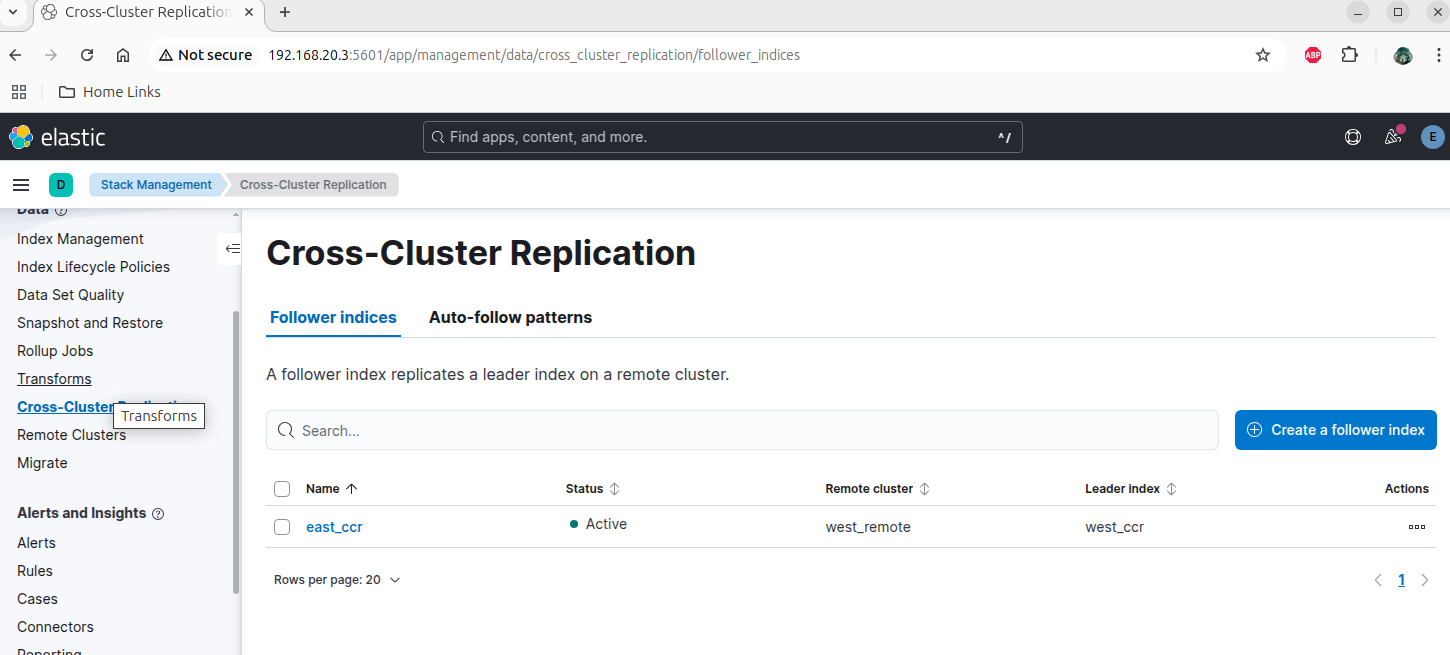
Cross-cluster Replication
Architecture
Configuration
Networking
The two clusters (West and East) are both implemented in Docker. Although West is a K8s implementation, the underlying architecture of Kind is in fact, Docker. Each cluster is in its own Docker network. For cross-cluster operations to function, we need to configure the linkage between these two Docker networks. The Docker commands below do just that.
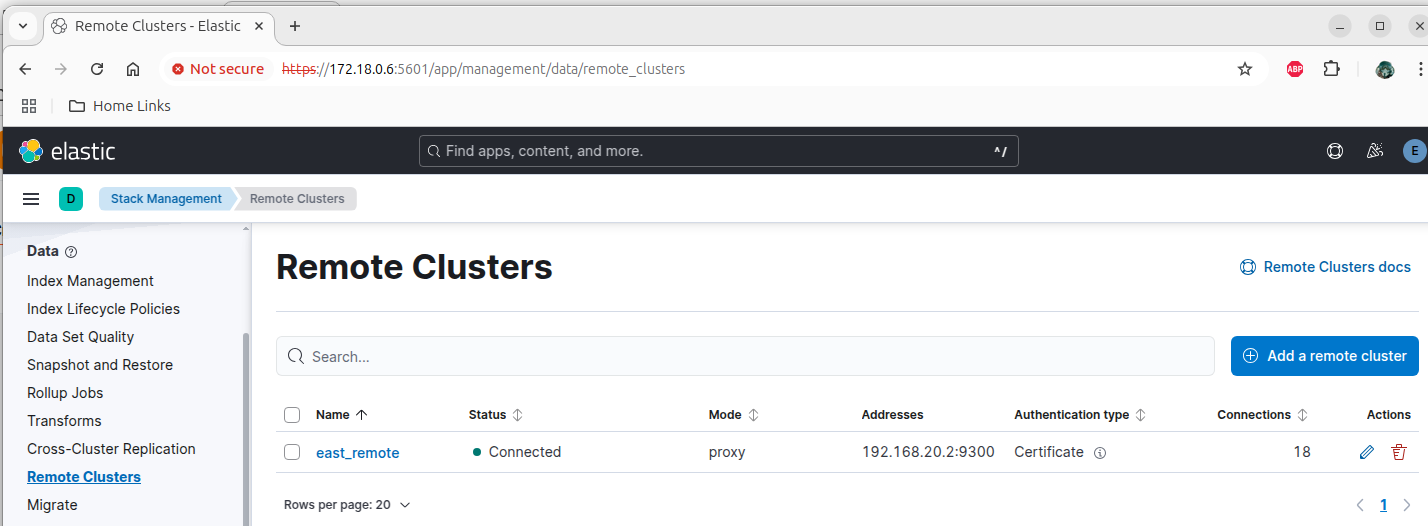
Remote Cluster Configuration
The West Cluster needs to be added to the East as a remote cluster. The commands below do that and then wait for the remote configuration to complete.
East Follower Index
In this scenario, we are setting up a leader index on the West cluster (named west_ccr) and its corresponding follower index on the East (named east_ccr). This will allow one-way replication from West to East.
Demo
At this point, true replication of the West index (west_ccr), including mappings (schema) has been accomplished. This can be verified with a simple Nodejs Elasticsearch client application that is located in the src/javascript directory.
Cross-cluster Search
Architecture
Configuration
Remote Cluster Configuration
Similar to the prior exercise of establishing the West cluster as a remote cluster on the East, the East cluster now needs to be configured as a remote cluster on the West.
Demo
At this point, everything is in place to execute queries that span the two clusters. A Python Elasticsearch client script is included in the src/python directory. That script executes a search against the West ES endpoint that spans both the west_ccs index on West and the east_ccs on East.